
There are three basic types of wood. Ring Porous, Diffuse Porous and Conifer. With the conifers there are those with resign ducts and those without. Then there is tropical wood. There are variations.

There are three basic types of wood. Ring Porous, Diffuse
Porous and Conifer. With the conifers there are those with resign ducts
and those without. Then there is tropical
wood. There are variations.
Source of all images on this page - TREES, ASSOCIATES, and SHIGO (2 CD set).

 Ring
porous wood such as, oak, elm, chestnut and black locust, are angiosperms that
have large diameter vessels in the first portion of the growth increment and
vessels of smaller diameter later in the growth increment.
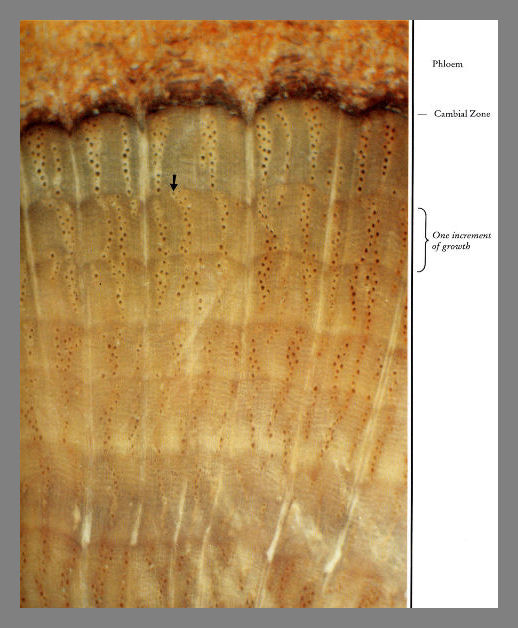
Ring
porous wood such as, oak, elm, chestnut and black locust, are angiosperms that
have large diameter vessels in the first portion of the growth increment and
vessels of smaller diameter later in the growth increment.

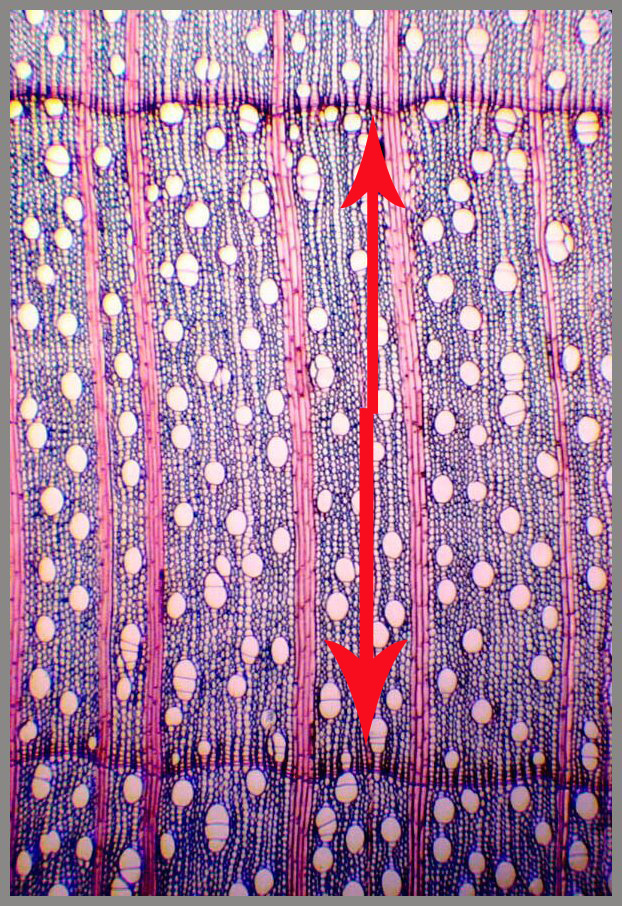 Here
we see one increment of a maple (between arrows) which is diffuse porous wood. The vessels
are diffused throughout the growth increment.
Here
we see one increment of a maple (between arrows) which is diffuse porous wood. The vessels
are diffused throughout the growth increment.
E.g., maple, apple, cherry, beech and holly and
the list goes on.

 Oregon Ash (Fraxinus latifolia)
Oregon Ash (Fraxinus latifolia)
Semi Diffuse Porous starts out growth as a ring porous and then becomes diffuse porous.
Something Different
 California
Live Oak - Quercus agrifolia
California
Live Oak - Quercus agrifolia
The anatomy of the live oaks - Quercus virginiana is southeastern USA and related species - is very different from white oaks and red oaks, yet they are usually grouped with the white oaks. The growth increments of live oaks does not start with large vessels. The vessel pattern is more similar to those formed in latewood of other oaks. Growth increments can be discerned, but with difficulty. The arrow shows where the radial line of vessels ends in one growth increment. The wood in Tanoak, Lithocarpus densiflorus is similar to wood in live oaks.

Conifers do not have vessels they have tracheids.

A Close up of a Conifer
The wood is made up of tracheids and fiber tracheids.

We have two basic types of conifer wood . Those with resign ducts and those without resign ducts. Then we have those which have resign ducts in the wood and those with resign ducts in the phloem (inner bark). Some in the wood (early or late wood) and some only when wounded (traumatic resign ducts). Here are some examples.
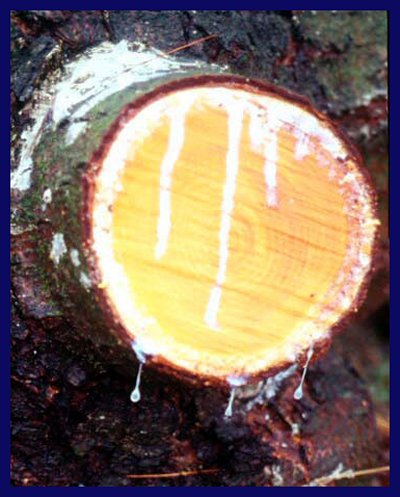

Pine Tree with Fresh Resigns. (NOT SAP)
White pine trees form resign ducts mostly in the late or summer wood.

The inner bark or phloem has produced resigns from resign ducts. The reddish brown substance. Remember resign ducks are enlarged parenchyma cells.
Spruces mostly do not form resign ducts until wounded.
Blue atlas cedrus (Cedrus atlantica), I have seen, is a conifer that can form resign ducts after wounding in the inner bark and current growth increment.
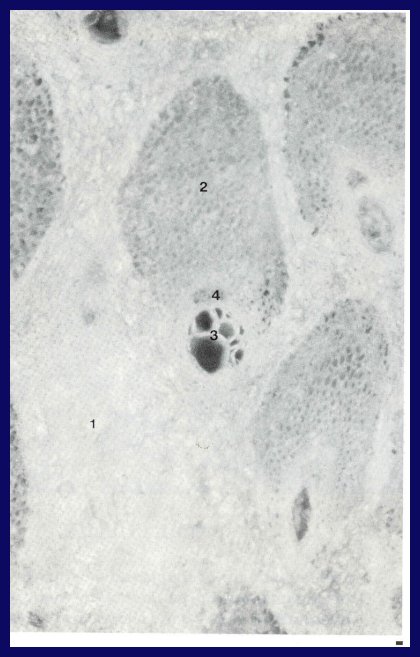
Solitare palm, Ptychosperma elegans
Thin walled parenchyma cells make up the soft ground tissues (1). Very tough strands of vascular bundles made up of thick-walled cells (2), contain the xylem (3) and phloem (4).
The tough strands within the soft ground tissues give palms unique abilities to bend without breaking during high winds.
Dictionary MAIN
PAGE
Text & Graphics Copyright © 2008
Keslick & Son Modern Arboriculture
Please report web site problems, comments and words of interest,
not found.
Contact